Interest in resorcinol diglycidyl ether didn’t just pop up overnight. Chemists began adapting epoxide chemistry in the mid-20th century to build adhesives and polymers with better heat and chemical resistance. Back then, resorcinol already had a solid reputation in resins. The step to link glycidyl groups to it followed the urge to blend phenolic backbone rigidity with the versatility of epoxy functionality. Researchers in Japan, Europe, and the US explored variations in hopes of creating formulations that handled more environmental stress or bonded trickier materials. Years later, the chemical took root in sectors eager for specific curing speeds and moisture resistance, such as coatings, sealants, and electronics. These early developments paved the road to today’s standards in resin technology, showing how chemistry can drive a material from the workbench to practical, scalable applications.
Resorcinol diglycidyl ether serves as a multi-functional reagent. Its main job falls in modifying epoxy-based adhesives, improving flexibility and strength. Manufacturers lean on it to impart weather resistance and to adjust viscosity in formulations where conventional epoxies struggle. Instead of sticking to one use, companies turn to it for electrical encapsulation, automotive assembly, or specialty coatings. Those who have handled batches know its liquid state simplifies mixing and dosing, especially compared to alternatives that come in solid forms or require high heat to blend.
The liquid at room temperature stands out with its clear to pale-yellow appearance and a noticeably pungent smell. It clocks in at a molecular weight near 266 g/mol, and carries a density a bit above water—this matters when weighing out portions for production. Typical resorcinol diglycidyl ether sits at a boiling point above 150°C (decomposes before boiling outright), and freezes below -20°C. Its two oxirane groups give it keen reactivity, particularly with amines and acids. Viscosity generally ranges from 30 to 60 mPa·s, manageable for most automated dispensing equipment. Solubility in alcohols, ketones, and aromatics allows for flexibility in cleaning and formulation. Notably, it reacts vigorously if severely overheated or mixed with strong acids, which always calls for experience and attention in process control.
Tech sheets for resorcinol diglycidyl ether list epoxide equivalent weight, purity (usually >97%), and water content (should be low to minimize side reactions). A low hydrolyzable chlorine level preserves stability when the resin hits metal surfaces or sensitive electronics. Production batches require tracking for batch number, manufacture date, expiry, and hazard class per GHS standards. On-site, labeling features GHS pictograms, hazard codes like “H315: causes skin irritation,” and proper handling instructions. Every shipment and storage area shows these details to keep everyone informed, especially those less familiar with the dangers of reactive epoxides.
Synthesizing resorcinol diglycidyl ether begins with resorcinol and epichlorohydrin in the presence of an alkali, often a solution of sodium hydroxide. The procedure runs under cool temperatures to limit side products. As glycidyl ether groups form, proper venting captures generated byproducts such as salt and excess epichlorohydrin. Controlled washing removes inorganic salts, then vacuum stripping purifies the mixture further. Anyone running the process has to monitor temperature, pH, and mixing rates constantly. Skipping these checks can throw off the epoxide value or leave behind unreacted precursors—both trouble for quality and safety. Each batch ends with a battery of chemical analyses—epoxy value, color, viscosity, and sometimes, GC-MS for impurities.
Chemists prize resorcinol diglycidyl ether for its dual epoxy groups. With amines, it crosslinks quickly, forming rigid or toughened networks for adhesives and coatings. Acid-catalyzed curing opens routes for specialty thermosets. Adding tougheners or plasticizers makes the cured resin more impact-tolerant. Blending with novolacs or other polyepoxides tunes curing speed and thermal behavior. Reacting with thiols, carboxylic acids, and anhydrides further broadens the material’s utility—each path carves out properties valued in composites, sealants, or even surface modification of nanoparticles. For customers needing specialty features like faster setting or higher resistance to environmental stress cracking, researchers twist the formulation by playing with catalysts or compatibilizers.
Trade literature identifies resorcinol diglycidyl ether by several names, like RDGE, 1,3-Bis(2,3-epoxypropoxy)benzene, or Diglycidyl ether of resorcinol (DER). Brands in Europe and Asia market it under proprietary labels—yet no matter the name, chemical structure and critical safety standards remain the same. Users in global supply chains quickly learn to match chemical names, brand variants, and CAS numbers to avoid accidental substitutions.
Handling this compound means more than following a checklist. Direct skin or eye contact can burn, so gloves and face shields belong on every workstation. Epoxy vapors cause respiratory irritation, so good ventilation and, for larger-scale work, full fume hoods come standard. While some users in past decades neglected personal protection, most companies now enforce rigorous hazard communication. Emergency showers, eyewash stations, and spill controls sit close by any work area. Disposal never goes straight to the drain; neutralization and certified hazardous waste collection apply across North America and Europe. Safety data sheets (SDS) build knowledge for both day workers and trade professionals, and ongoing training remains crucial as process tweaks or new applications emerge.
Resorcinol diglycidyl ether keeps showing up in places where toughness and chemical durability win the contract, like in civil engineering adhesives for bridges, consumer electronics encapsulants, or even demanding marine coatings. Engineers use it when weather swings hurt regular epoxies and where plastics need extra resilience against UV, salt, or solvents. Artisans and industrial techs alike rely on it in laminating specialty woods or compositing advanced fabrics. From first-hand experience in pilot plant scale-ups, process tweaks to use RDGE often lead to stronger, longer-lasting bonds where conventional choices failed. Keeping defects and costly repairs in check pays off for manufacturers and, ultimately, for everyone at the end of the supply chain.
R&D with resorcinol diglycidyl ether involves more than test tubes and notebooks. Lab teams scrutinize new curing agents or additives to push mechanical properties or accommodate recycled fibers and plastics. Data from field trials drive updates in formulations—especially as industry seeks lower VOC emissions and faster setting times. Trends in smart materials or greener chemistries nudge scientists to explore bio-based sources for epichlorohydrin or resorcinol itself. While legacy systems once dominated, the push for sustainability now motivates regular audits on raw materials and long-term performance of finished products in real conditions. This close feedback loop between lab, manufacturing floor, and end user shapes each new generation of materials.
Toxicologists have tracked the hazards of both epoxides and resorcinol class molecules for decades. RDGE, like most glycidyl ethers, can cause skin and respiratory irritation, and repeated mishandling increases risk of sensitization. Early animal studies flagged some concerns with chronic exposure and potential organ toxicity, although toxicity rankings fall below that of some halogenated compounds. Nevertheless, its breakdown products and production residues draw careful scrutiny in environmental studies—especially around manufacturing waste streams. Regulatory agencies require ongoing reporting and independent verification to reassure both workers and communities near plants.
The story isn’t finished yet. Growing demand for safer, healthier building materials nudges the industry to create ever-safer formulations with lower emissions, and more predictable curing profiles. Digital manufacturing and additive printing also require resins with custom flow, reactivity, and strength. The chemistry behind RDGE offers flexibility: small changes in the molecule or the blend can create tailored properties for emerging applications in aerospace, electronics, or smart infrastructure. Green chemistry initiatives spark efforts to use renewable feedstocks and improve recovery from manufacturing waste. As global standards evolve and downstream users ask tougher questions about provenance and sustainability, progress will revolve around openness, research transparency, and responsive adaptation—core elements for anyone committed to responsible, effective innovation.
Factories don’t run without strong adhesives, and the need for bonding grows every year. Resorcinol diglycidyl ether steps up in this arena. This compound gives epoxy resins the muscle to withstand tough conditions found in construction and automotive work. It serves as a key ingredient in making glues that hold up against heat and chemical exposure.
From a technical point of view, I’ve worked with epoxy systems both in small workshops and on construction sites. Consistency in curing, resistance to cracking, and durability often come down to the additives in those formulations. Resorcinol diglycidyl ether tends to deliver a solid performance because of its chemical structure. Studies have shown its cross-linking abilities toughen bonds, especially where wood, metal, or concrete need to stay united for decades. This isn’t just theory; the difference is visible over time as some structures resist weathering far better than others.
Companies also like this ether because it blends well with other epoxies. Formulators can adjust for more flexibility or rigidity as the job demands. That kind of control makes repairs or original construction stronger from the start. Over the years, I’ve heard from contractors who have torn apart old builds—the bonds using this chemistry often outlast the materials being held.
Electronics manufacturers rely on materials that shield and protect against electrical currents and moisture. Resorcinol diglycidyl ether enables the making of conformal coatings—a clear layer sprayed onto circuit boards that stops short circuits and corrosion. Factories that churn out consumer electronics test these coatings in harsh conditions including salt fog, high humidity, and temperature swings.
My own time troubleshooting device failures taught me that cheap coatings fail quickly, leading to phone or tablet breakdowns before their time. Better quality resorcinol-based epoxies reduce warranty claims and frustrated customers. Technical datasheets from suppliers show that high-purity chemicals lead to higher performance, with fewer failures due to delamination or moisture intrusion.
It’s not all sunshine. Resorcinol diglycidyl ether demands respect in the factory. People mixing it into epoxy batches wear gloves, respirators, and goggles. Skin sensitization and irritation appear in safety warnings published by major suppliers; chronic exposure brings real concerns. Regular industrial-health audits keep workers safe by controlling how much vapor escapes and reminding everyone to stick to the safety gear routine.
Looking back, I’ve seen both good and bad: plants with strict safety programs post much lower rates of chemical exposure and complaints. The knowledge is out there—authorities like OSHA and REACH publish plenty. Following these rules isn’t about red tape but about real people staying healthy enough to work for years. For those running small shops, staying informed and sticking with the right protective gear makes all the difference.
In industry, progress means finding ways to keep strengths like those of resorcinol diglycidyl ether while steadily cutting down on workplace risk. Research into greener alternatives continues, but for now, this versatile compound remains in heavy rotation wherever strength, bond, and toughness matter most.
Resorcinol diglycidyl ether often finds a home in specialty adhesives, coatings, and electronics. It packs chemical punch, so respect needs to be paid before opening up a drum or vial. The material brings potential for skin sensitization and respiratory irritation. Not every chemical brings out rashes or coughing fits, but this one has a stubborn track record. Researchers and workers share stories about unexpected rashes and headaches after skipping gloves or dust masks. Personal experience with skin allergies has taught me how minor exposure can trigger long-lasting reactions. A small lapse one day can mean wearing bandages for weeks.
Let’s talk gloves, goggles, and lab coats. Nitrile gloves—no thin latex—hold up better against this stuff. Chemical-splash goggles keep stinging droplets out of eyes. Lab coats or coveralls mean you won’t have to toss your jeans after a spill. Boots cover up sock-lines skin and keep shoes from soaking up spills. Face shields add another layer, especially for mixing or pouring. Once after a hurried clean-up without goggles, I learned that watery burning eyes aren’t worth cutting corners. Losing a day to recovery doesn't improve productivity.
Sprinting past the fume hood saves maybe a minute in the morning. A fume hood grabs vapors and fine droplets, sending them out of your breathing space. Local exhaust fans around mixing or decanting setups can make a difference. No one wants to trust their lungs to luck. Installing splash guards can also keep errant droplets off arms and walls. Friends in the industry have told me about switching to dedicated ventilated workbenches—workers started feeling better, absenteeism dropped, and backlogs disappeared.
Proper storage keeps everyone a little safer. This one stays sealed, away from acids, bases, and oxidizers that trigger nasty reactions. Dedicated chemical cabinets—not the staff fridge or shared supply closets—keep things organized and limit cross-contamination. It's really annoying to find sticky residue on shared doorknobs or countertops, especially when these surfaces get overlooked during clean-up. If a spill happens, folks need absorbent pads and neutralizing agents nearby. Quick mop-ups followed by soap and water reduce the chances something lingers. Every so often, drill a spill response with the team—muscle memory kicks in when nerves start fraying.
Safety documents tend to gather dust somewhere in the back office. Regular training and walk-throughs beat a stack of printouts. Let people talk through what’s tricky for them, because everyone works a little differently. Communication gaps often lead to sloppiness. Labels in plain language—no squinting at faded barcodes—help spot risks fast. Pair newbies with veterans, so experience and habit get passed down. Sometimes, taking five minutes for a demonstration or storytelling session makes the difference between safe handling and a rushed shortcut.
Not every irritant shows itself right away. Redness and swelling might appear hours or even days later. Setting up a process for reporting symptoms and seeking medical attention means issues don’t get shrugged off. No one enjoys paperwork or clinic visits, but early attention can prevent bigger problems. Good hygiene—washing hands before lunch, keeping food out of chemical areas—cuts down risk further. I’ve found that being strict about these routines pays off: my workdays run smoother, and co-workers trust the environment more.
Respecting chemicals has to be part of every day, not just safety audits. If someone sees a shortcut or risky behavior, they need to speak up, no lectures needed. Honest reminders, quick corrections, and teamwork drive safer habits. It only takes one mishap to remind an entire crew why these rules aren’t just bureaucracy—they’re protection for people, equipment, and future opportunities.
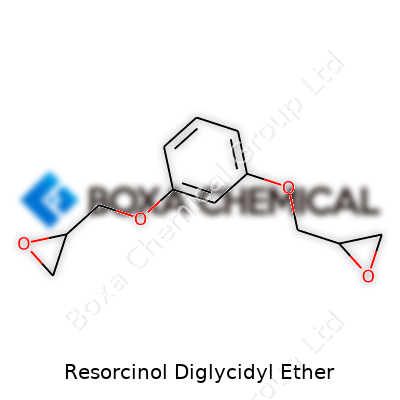
Resorcinol diglycidyl ether brings together two main chemical ideas: resorcinol and the epoxide group you find in glycidyl ethers. Chemists call its structure C12H14O4. Its backbone uses resorcinol, which is a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups sitting next to each other. These hydroxyls react with epichlorohydrin to form the glycidyl ether groups. Now, on both sides, the ring wears an epoxide “cap,” setting it up for plenty of reactivity down the line.
In plain talk, the molecule starts as a six-carbon ring with two oxygen-hydrogen groups. Through a reaction, these spots swap hydrogens for little three-membered epoxy “arms” called glycidyl groups. Those arms make the molecule interesting to industry because they let it link up with other chemicals and cure into tough networks.
Epoxy resins rely on small building blocks like this one. Take adhesives and coatings, for example. Manufacturers seek out resorcinol diglycidyl ether because its structure allows the resin to harden evenly and resist chemicals. The molecule’s benzene ring brings heat resistance, and the epoxide groups snap open to react with hardeners, producing a web of strong bonds. The cured product stands up to water and solvents much better than cheaper alternatives.
One overlooked fact: that two-part epoxy kit on hardware shelves owes a lot to compounds just like this. Cost and performance steer companies toward resorcinol diglycidyl ether when reliability can’t take a back seat. Electronics, construction, and even aircraft repairs use it to hold things together or to create coatings that shrug off harsh environments.
Working with reactive chemicals brings up safety questions. Both resorcinol and epoxides show risks. Anyone handling resorcinol diglycidyl ether ought to wear gloves, goggles, and work in a ventilated place, simply because contact can cause irritation and allergies. Studies highlight possible skin effects and point out that strong epoxide groups make it easy to overexpose the skin or lungs to risks during large-scale use.
Precautions in industry settings matter. Factories have switched to closed systems for mixing and dispensing these resins, sharply reducing exposure. Training and equipment updates lowered reported workplace incidents according to several occupational health studies in North America and Europe. The science says, treat this compound with respect. Skimp on ventilation or personal gear, and problems show up fast.
Alternatives sometimes get attention, especially as green chemistry pushes forward. Water-based systems, modified natural resins, and lower-toxicity epoxies have started cropping up, but for some demanding situations, the combination of strength and resistance found in resorcinol diglycidyl ether-based epoxies still sets the standard. Recycling and reclaiming closed-loop systems from cured epoxy scraps also make use less wasteful. Research points to more “bio-derived” glycidyl ethers arriving soon, which could keep performance high while shrinking the environmental footprint.
Anyone involved in chemistry, manufacturing, or building knows substances like resorcinol diglycidyl ether do real work. The structure tells the story: ring for toughness, epoxide arms for bonding, and responsibility on the user’s side for both safety and innovation.
Resorcinol diglycidyl ether carries more risks than common chemicals at home or work. This compound can cause skin reactions, release harmful vapors, and even create fire hazards in the wrong conditions. Having worked with chemicals for years, I pay close attention whenever these special handling requirements come up. The smallest shortcut, like storing a drum near a window or beside heat sources, can lead to much bigger problems.
Leaving resorcinol diglycidyl ether where sunlight or heat builds up raises risks fast. This chemical can degrade, expand, or build pressure inside containers. At a lab I once worked in, someone set a box near a furnace room; fumes appeared overnight. Keeping it between 2°C and 8°C avoids most temperature-driven issues. Refrigerated storage, with secure shelving and clear labels, works much better in the long run. High humidity and hot spots—think unventilated basements or upper storage racks—should always be avoided.
This chemical reacts with strong oxidizers and open flames. Storing it near solvents, cleaning supplies, or break areas makes little sense. I remember cleaning up after a spill once, and static sparked from synthetic work boots—small lapse, near disaster. Good practice always separates storage areas well away from sources of ignition or strong chemicals that could interact unpredictably. Grounding shelves and ventilation fan controls helps, especially during hotter months.
Poor air circulation means vapors hang around. In tight storage closets, vapors build up, potentially harming people who open the door or walk past. Installing an exhaust fan or keeping the are open to airflow goes a long way. A well-marked chemical cabinet makes the most sense for small containers, with spill trays underneath to catch drips. At one facility, we had dedicated flammable cabinets lined with absorptive mats—which made spill cleanup much less stressful. Spills get managed quickly, lowering the risk for colleagues working late or janitorial staff sweeping through at night.
Accurate, large-font labeling makes all the difference. Chemical names, hazard pictograms, and date of arrival need to be front and center. In one case, two white bottles sat side-by-side on a shelf, and a rushed worker grabbed the wrong one. The result: a burned countertop and plenty of paperwork. Every company or lab should check labels monthly and replace anything faded or torn. It’s such a simple step and cuts down on accidents and mix-ups that lead to injuries or chemical reactions.
Minor spills can cause big problems if left unattended. Having a clear spill protocol, quick-to-reach absorbent kits, and disposable gloves in the same storage space makes response time quicker. Every site I’ve worked at required that waste get separated and taken out to hazardous waste streams—never poured down a drain or tossed in regular trash. Collection timers and logbooks keep waste from piling up and becoming forgotten hazards.
Every person who handles, stores, or transports chemicals like resorcinol diglycidyl ether needs current safety training and easy access to chemical safety data sheets. Small habits—double-checking lids, storing only in recommended containers, and updating logs—make everyone safer. This chemical can be managed easily, but the responsibility never stops. Following best practices doesn’t just protect people on-site; it protects everyone who comes in contact down the line.
Resorcinol diglycidyl ether turns up in some demanding manufacturing jobs. Plenty of factories rely on it for making high-strength adhesives and industrial coatings. I’ve spent enough days around shop floors to know that chemicals deserve respect, especially those carrying epoxide groups like this one. Lab tests flag this compound as both an irritant and a potential skin sensitizer. That’s not scaremongering – people really do get rashes, cracking hands, and allergy flare-ups from not handling it with care over long shifts.
Contact with resorcinol diglycidyl ether doesn’t just end with a nasty rash. Sensitization worries me most. People start out fine, but repeated, even minor, skin contact can trigger a lifetime allergy. Once that happens, you can end up unable to go near jobs that use anything related to epoxies. Respiratory symptoms sometimes follow if fumes build up in a poorly ventilated area. Engineers in the industry today are up against the same challenge we faced years back: keep exposure down, or someone pays for it with their health.
Digging into published toxicology reports, I learned that swallowing or inhaling the stuff harms lungs, throat, and stomach. Epoxies, including resorcinol diglycidyl ether, often get flagged in medical studies for possible links to long-term illness. Regulatory bodies, like the European Chemicals Agency, keep a close watch here. Many employers carry out risk assessments, swap in gloves and fume hoods, but accidents still happen.
Some researchers express concern about reproductive risks. Consistent, high-level exposure in animals brought up red flags. Nothing dramatic from low-level, single exposures, but repeated careless handling builds risk over time. Staying in the industry taught me precaution beats regret. Nobody wants a chemical injury shadowing their working life.
Environmental hazards often hide in plain sight. Resorcinol diglycidyl ether falls into that pattern. Once it gets into water or soil, breakdown moves slowly. Epoxy resins stick around for a while, and sometimes, wildlife takes the hit. Even at low concentrations, fish and other water critters can show signs of stress or reproductive problems. Waste rules push companies to treat every drop like it matters. Disposing of it through normal drains spells trouble for local rivers and streams, which face toxic build-up before anyone notices a problem.
I’ve seen smart changes make a difference. Using enclosed systems, training workers early, and keeping up with the latest research helps lower risks. Substitute less toxic alternatives whenever possible. If replacement can’t happen, require full protective gear and regular medical checks. Plants I worked at locked down chemical storage and used clear labeling to stop mix-ups. More inspectors and surprise audits put pressure on everyone to get this right.
Green chemistry breakthroughs could eventually move us past materials with a long toxic tail. Until then, strict workplace rules and responsible disposal practices provide the strongest shield against harm to both people and the planet.
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 4-[2-(Oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)ethoxy]benzene-1,3-diol |
| Other names |
1,3-Bis(2,3-epoxypropoxy)benzene 1,3-Phenylenebis(2,3-epoxypropyl)ether Diglycidyl resorcinol ether RDGE |
| Pronunciation | /ˌrɛˈsɔːrsɪnɒl daɪˈɡlɪsɪdɪl ˈiːθər/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 101-90-6 |
| Beilstein Reference | 474156 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:140697 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2044913 |
| ChemSpider | 14247081 |
| DrugBank | DB14006 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 03-2119981513-47-0000 |
| EC Number | 603-862-8 |
| Gmelin Reference | 104611 |
| KEGG | C19587 |
| MeSH | D019215 |
| PubChem CID | 11497 |
| RTECS number | VS8575000 |
| UNII | U8H0A7P58B |
| UN number | UN2922 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID2020204 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C12H14O4 |
| Molar mass | 246.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow transparent liquid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.25 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Soluble |
| log P | 0.5 |
| Vapor pressure | 0.02 mmHg (25 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.8 |
| Basicity (pKb) | pKb: 13.23 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -9.6e-6 cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.543 |
| Viscosity | 50-60 mPa·s (25 °C) |
| Dipole moment | 2.67 D |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | D11AX06 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful if swallowed, causes skin irritation, causes serious eye irritation, may cause an allergic skin reaction. |
| GHS labelling | GHS05, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS05,GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | Harmful if swallowed. Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause an allergic skin reaction. Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects. |
| Precautionary statements | Precautionary statements of Resorcinol Diglycidyl Ether are: "P261, P264, P272, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P333+P313, P362+P364, P501 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | **Resorcinol Diglycidyl Ether NFPA 704: 2-2-1** |
| Flash point | 109°C (228°F) |
| Autoignition temperature | 250°C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 (oral, rat): 2,590 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): 1,130 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
| PEL (Permissible) | PEL: Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 0.01 ppm |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds |
1,3-Benzenedimethanol Resorcinol Phenoxyethanol Epoxy resin |