Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether first came onto the industrial scene during a time when chemists started searching for specialty chemicals to handle rising demands in resin manufacturing, adhesives, and coatings. The roots trace back to the mid-20th century, a period marked by rapid innovation in organic synthesis. Researchers were drawn to the phenolic backbone of resorcinol, and by modifying it with ethylene oxide to attach hydroxyethyl groups, industry gained a new compound with valuable solubility, flexibility, and reactivity. It took years of trial and error, but the resulting molecule carved a place for itself thanks to reliability and manageable handling compared to volatile alternatives.
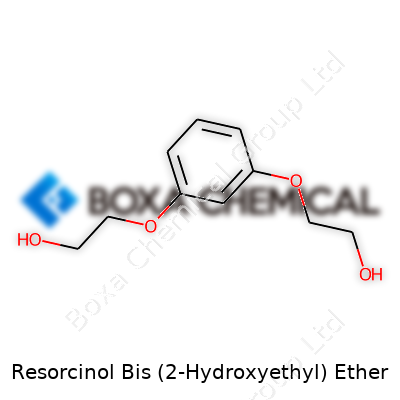
Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether stands out in the chemical sector as a specialty building block for polymers and resins. The structure involves a resorcinol core linked through two –CH2CH2OH arms, which boost the water compatibility and help blend into various formulations. This material suits resin crafters looking for a di-functional, fairly stable additive, especially in fields needing toughness and resistance against environmental stress. From electrical laminates to advanced coatings and adhesives, the product supports longstanding and emerging manufacturing challenges.
In its pure form, Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether appears as a colorless to pale yellow crystalline solid. People handling it notice a characteristic faint phenolic scent. Melting point sits between 95-100°C, with a boiling point usually above 280°C. The molecule dissolves readily in water and common organic solvents, which simplifies formulation work compared to less polar bis-phenolic systems. Molecular weight hovers around 246 g/mol. Chemically, the substance resists spontaneous oxidation in dry air, but exposure to acids or bases can lead to hydrolysis and degradation. Its diol character means that it takes part in typical ether reactions, nucleophilic substitutions, and esterifications.
Quality specs for this ether focus on purity—most grades hit over 98% assay. Water content and levels of mono-hydroxyethylated byproducts stay tightly controlled to avoid process disruptions. Standard labeling under GHS includes an irritant warning, though the compound remains less hazardous than raw resorcinol. For identification and safe storage, labeling includes batch number, net mass, and recommended shelf life (usually about three years in a sealed container away from moisture and light). Transport documents classify it as a non-dangerous good in most jurisdictions, although individual country rules still govern workplace exposure limits.
A lot of the industry relies on the classical method: treat resorcinol with excess ethylene oxide in the presence of a base—often sodium hydroxide. This batchwise reaction heads up to about 50-80°C to keep phase separation under control and to manage exotherms. After reaction, chemists neutralize the remaining base and extract the desired ether. They typically purify the product through several washes and vacuum distillation. By adjusting reaction time and ethylene oxide ratios, manufacturers balance throughput and selectivity, aiming for minimal formation of unwanted mono- or tri-substituted byproducts.
The molecule's diol arms invite all sorts of functionalization. In lab practice, the compound reacts with diisocyanates to form tough, flexible urethane networks. Its two hydroxyethyl groups undergo esterification with acyl chlorides, opening doors to new surfactants and emulsifiers. Under mild oxidation, chemists get to dial in nuanced changes to electronic properties, which proves helpful for specialty electronic coatings. One of the standout features: preserves the core aromatic stability from resorcinol, so the ether faces less breakdown under heat or UV than simpler linear diols.
Chemists and suppliers refer to Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether by a range of names, including 4,4'-Dihydroxy-3,3'-bis(2-hydroxyethoxy)biphenyl and REHE. Other catalogues list it under CAS number 10138-41-7. In my experience, the simplest “Bis(2-hydroxyethyl)resorcinol ether” label covers most technical documentation, but local distributors sometimes sell it as “DEHER” or “Resorcinol Di(2-hydroxyethyl) Ether,” so keeping track of synonyms avoids misorder or confusion during procurement.
Workplace standards expect fume hoods for powder handling and gloves for skin protection. Though the ether doesn’t pack the punch of volatile solvents or free resorcinol, it can irritate skin, eyes, and upper respiratory tract. Chronic exposure brings low but real toxicity risk, so longer jobs need goggles and protective clothing. National authorities set permissible exposure limits—usually mirrored by European REACH or OSHA policies. Spills get tackled with absorbent materials and produced waste heads to chemical incineration or controlled landfill, per modern environmental guidelines. Training for those handling the material covers not only direct exposure but also how to respond to lab accidents—especially since handling ethylene oxide or strong base in the prep stage raises separate hazards.
In composite resins for electronics, Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether adds strength and moisture resistance, key for printed circuit boards and automotive coatings facing regular heat stress. The adhesive sector values its dual hydroxyethyl arms, which toughen urethane networks and allow novel crosslinking in two-part glues. It also appears in select pigment dispersions, helping to stabilize colloidal mixtures in water-based paints. Researchers have taken the material into polymer modification—changing plasticity and impact performance. In specialty surfactants, chemical suppliers pursue unique emulsification profiles not possible with standard linear glycols.
Laboratories keep a close eye on new methods for preparing Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether to improve yield, lower waste, and avoid dangerous side reactions. Modern green chemistry work explores catalytic systems that dodge the need for massive bases or toxic solvents. Polymer scientists test new copolymers using the ether to offer specialty plastics better resistance against UV aging and chemical attack. Biomedical engineers run trials on modified versions hoping to unlock biocompatibility for drug delivery or medical adhesives. R&D stretches into electronics as newer circuit board designs challenge heat thresholds and chemical inertia. Projects pop up every year in major journals and patent filings, often blending classic chemistry with new engineering concepts.
Animal studies indicate the ether has low oral toxicity, with large doses provoking mild liver enzyme changes but not outright organ damage. Long-term contact studies show that skin absorption remains limited, but repeated exposures risk dermatitis for sensitive workers. Inhalation studies in rodents suggest adverse effects only at concentrations higher than most workplaces will see. Most regulatory reviews put the ether solidly below the risk levels of phenol or monochlorinated resorcinols, which is a reassuring result for plant operators and people working on the line. Wastewater treatments need to capture residuals, as aquatic life develops chronic stress when concentrations climb above certain thresholds, so discharge rules place strict caps on effluent.
Looking ahead, Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether sits in a sweet spot for sustainable chemistry. Biobased feedstocks for both resorcinol and ethylene oxide will shift this product’s footprint downward, meeting tough new ecolabel targets pressed by regulators and consumers. The electronics field expects demand to rise as 5G, EVs, and smart textiles push polymer needs into unfamiliar territory—requiring materials that won’t break down in harsh use. Coatings and adhesives developers want to unlock new green curing processes, and this ether holds promise thanks to its balanced reactivity and manageable safety profile. Academic partnerships and industrial big players both drive ongoing innovation, so the chemical stands ready to anchor several years of creative product launches and manufacturing shifts.
Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether, or RBHEE as it’s sometimes called, is a chemical many outside the industry have never heard of, yet it finds its way into spots that touch lives daily. I spent my early years working in a small plastics fabrication shop, where resins and additives made the difference between a finished part cracking in the sun or lasting years. From those hands-on days, I've seen how this compound weaves its value into products we use, often without a second thought.
Manufacturers reach for RBHEE to dial in the toughness, chemical resistance, and performance of epoxy resin systems. Folks rely on it in the adhesives keeping wind turbines and airplanes together, or outdoor coatings standing up against weather and UV. I remember fixing a fiberglass boat hull using epoxy resin boosted by specialty additives. RBHEE kept the mix from snapping when temperatures soared or dropped. Its molecular structure, rich with hydroxy groups, hooks into the larger resin network—making adhesives and coatings tougher against abrasion and moisture penetration. Boeing and other aerospace leaders point to additives like RBHEE for advancing lighter, more resilient composite parts.
In the world of synthetic rubber, RBHEE finds steady work. Tire makers use it to strengthen bonds within the rubber matrix, directly impacting how long tires stay on the road. Over the past decade, as demand for longer-lasting, fuel-efficient tires grew, chemical engineers leaned on compounds like RBHEE to let rubbers stay flexible and strong. This reduces blowouts and extends the lifespan of tires for everything from motorcycles to commercial trucks.
Smartphones, laptops, and circuit boards depend on reliable insulation. RBHEE helps create tough, flame-resistant laminates insulating sensitive connections. With gadgets only shrinking and heat buildup rising, thermal durability counts more than ever. A semiconductor engineer once showed me a burned circuit board destroyed by faulty insulation. Implementing epoxy blends containing RBHEE fixed that, eliminating premature failures in the next batch of chips.
Architectural paints and floor sealants benefit from RBHEE too. By cross-linking with other ingredients, it grants longer wear, glossier finishes, and improved resistance to chemicals and traffic. In high-traffic hospital corridors, floors treated with sealants that include RBHEE stay clearer and require less maintenance—saving real dollars for facility managers.
Sustainability always lingers at the edge of chemical production. While RBHEE delivers big wins in performance, its production does involve petroleum-based feedstocks and energy-intensive methods. Modern producers look for ways to reuse waste and cut emissions, but more progress will come from industry investment and transparent supply chains. Companies that disclose their safety and environmental data, and who invest in sustainable raw materials, build trust with customers and regulators.
The next step falls on both manufacturers and policymakers: keep advancing high-performance materials while pushing for cleaner chemistries. Transparency around ingredients helps customers make informed choices, whether they’re buying bike helmets for their kids or materials for public infrastructure. More investment in recycling and safe chemical alternatives will set the pace for the next generation of industrial growth.
Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether has the formula C14H18O4 and a molecular weight of 250.29 g/mol. Demystifying numbers like these matters more than it sounds. These details help researchers, manufacturers, and even health advocates keep a close eye on safety and performance. In the wider world, few folks linger long on a compound’s formula, but its roots shape everything from cost to risk factor to environmental footprint.
Chemical choices have always played a major role in how groups turn ideas into finished products. This ether, for example, often ends up as part of industrial resins, adhesives, or specialty coatings. Each touchpoint brings its own challenges and questions. Many factories look for materials that hold up to harsh temperature swings, resist yellowing, or bond strongly without breaking down. The unique structure of Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether gives it important stability. Its molecular weight explains why it flows, cures, and responds the way it does. This isn’t just a “lab thing”—better design means longer lifespans for coatings, which means less waste and rework down the line.
Safety rises to the top, always. Many industrial chemicals carry potential risks if they interact with skin, eyes, or lungs. Resorcinol derivatives as a family draw extra scrutiny. Reliable global studies place skin irritation, potential allergies, and other acute effects on the radar for people who use this ether at high concentrations or over long periods. That’s why responsible companies invest in clear labeling and worker training. In regions with strong chemical safety rules, labels and data sheets must give up-to-date toxicity data, personal protection tips, and outline what to do in case of emergencies. Testing continues to clarify if, and how much, a particular chemical might linger in waterways or soil. Transparency helps keep both plant workers and communities safer.
Several regulatory agencies keep tabs on how compounds like this one flow through supply chains. The EPA in the U.S., ECHA in Europe, and similar bodies push for more rigorous chemical tracking and better hazard information. Following rules, though, only sets the floor. The world needs broader adoption of green chemistry, giving rise to alternatives that can keep up in performance but minimize exposure risk or pollution. Solvents or curing agents sometimes get swapped with greener cousins based on new scientific findings.
Better science education helps bridge the gap between chemical engineers and everyone else—cleaner products demand that more voices join the conversation. Engineers can use resources like PubChem and peer-reviewed journals to compare data points and find trade-offs worth making. Routine audits and user feedback loops help catch missteps before they hit the headlines. Community outreach, built on plain language and real-world stories, spreads awareness. Open dialogue rooted in data and daily experience shapes the next chapter for chemicals that people often take for granted.
Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether tends to show up in labs and factories with a role in making things like polymers, adhesives, and specialty resins. Few people outside a chemistry field ever mention it by name, but folks who handle it must think about what this substance means for safety. I remember my early days in the industry, watching seasoned technicians keep a wary eye on bottles with complicated labels. Their concern was not just habit. It had roots in clear lessons from occupational health.
Facts help more than hearsay. Looking through the available safety data, this compound has some clear markers: it can irritate skin, eyes, and the respiratory system with exposure. Anyone opening a drum or mixing a batch can breathe in mist or dust. It is not classified as carcinogenic or acutely toxic like some notorious industrial chemicals, but the immediate effects matter. OSHA and NIOSH outline steps that keep folks safe, like gloves, goggles, and good ventilation. Weakness in those barriers can lead to discomfort—red eyes, itchiness, a cough that sticks around.
Long-term data looks thin. Most reports point out that people should avoid chronic or repeated exposure just in case. No one wants to wait for solid proof about long-term effects if a simple mask and careful work keep trouble away.
Not every chemical catches fire easily. This one sits in a middling zone—not as risky as gasoline, not as gentle as water. High heat gives off fumes that can irritate or worse. A spill on the shop floor can move into drains and waterways because it dissolves well. The fish and algae downstream don’t need surprise chemical baths. One study shows moderate aquatic toxicity. It’s not the world’s worst, but enough to warrant careful storage and cleanup practices.
Lab managers or plant supervisors don’t trust luck. Practical safety steps serve as the real first line of defense. Clear labeling stands out. Knowing what you’re working with, grabbing a pair of nitrile gloves, and keeping eyewash stations easy to reach—these details protect health in busy environments. Employees at small shops sometimes skip fit-for-purpose fume hoods, not seeing the value. My old crew learned through one minor accident that a working exhaust fan means the difference between a headache and a good, ordinary shift.
Disposal practices deserve focus too. Pouring waste down the sink seems quick, but those chemicals don’t vanish. Following disposal regulations may slow things down, but it stops trouble far from the company doors.
After years in settings with a thousand moving parts, I see that process wins over wishful thinking every time. Chemicals with irritant properties do not respect shortcuts. Safety rules are written in pain, not on a whim. Solid training, a safer workspace, and personal gear build a path through risk. Companies should take the time to share what can go wrong—real examples stay in memory longer than a warning sign.
Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether has its place in manufacturing and labs. Respect for its risks keeps people healthy and businesses running. Simple protection and responsible handling turn a hazardous material into just another part of the job, not a headline waiting to happen.
Working in a lab has taught me that small mistakes can trigger big problems, even before the real work begins. Anyone who's had a close call with improperly stored chemicals knows the stress it brings—not to mention the risk to health and research outcomes. Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether gets used in specialty resins, adhesives, and some hardeners, so it pops up often enough in all sorts of industrial and research settings. Treating it casually doesn’t sit well with anyone who’s witnessed the fallout from lax storage or handling.
A lot of labs keep Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether in tightly closed containers, and for good reason. Moisture and reactive chemicals have a way of finding an opening, so keeping the container sealed stands as the first line of defense. Proper labeling does more than tick a box on a checklist; it saves confusion in the heat of an emergency.
This compound prefers cool, dry spots—think between 2°C and 8°C, away from direct sunlight. Most lab refrigerators or dedicated storage cabinets fit the bill. Strong acids, strong bases, and oxidizers should not share space, since they can line up trouble both for the chemical and for anyone nearby. I once saw a rookie mistake—resins stacked near oxidizers in a high school lab cabinet. Minor spill, but the stink and staff panic taught everyone a lesson in chemical neighbors.
Invest in storage shelving made from materials that don’t react easily. Stainless steel and powder-coated shelving outlast cheap metal that might rust or corrode. Ventilation means more than just opening a window now and then. Flammable safety cabinets with proper ducting make sure fumes don’t build up, putting the whole building at risk.
Handling Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether goes beyond just putting on a lab coat and calling it a day. Gloves, goggles, and good ventilation stand as the minimum. Nitrile gloves work well, as they keep the compound away from skin. If spills reach skin or eyes, run for the eyewash or safety shower without hesitation. One thing I've learned over years of lab work: people hesitate in emergencies, thinking they’ll look silly. It’s not silly if it prevents a trip to the ER.
Pouring or mixing needs a fume hood or at least a well-ventilated bench. Inhalation of vapors or fine dust can sneak up with repeated exposure, not always causing immediate symptoms but building up over time. Face shields go a long way during any transfer or bulk handling, especially with open containers.
Waste disposal has tripped up many experienced teams. Pitching used materials or spilled product in the regular trash spreads risk beyond the lab. Regulations call for secure, clearly marked waste bins for such chemicals. Sending waste to a licensed hazardous disposal service fits both company policy and the law, but more importantly, it lets everyone sleep a little better at night.
Overlooking best practices with Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether doesn’t just put health on the line; it puts research, jobs, and reputations at risk. A single spill, an overlooked label, or one lazy clean-up cuts deep into budgets and trust. Training, clear signage, and steady habits drive safety, not once-a-year reminders or dusty binders. For me, following these steps isn’t about compliance—it’s about respect for the next person who opens that cabinet, their family, and the world outside.
Standing on the production floor, I’ve seen what a difference a tiny impurity can make. Chemical processes tend to have little room for surprises. Ask anyone who’s watched a batch of resin go off-spec early on just because someone skipped a simple purity test. Purity, especially with specialty chemicals like Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether, isn’t a fine print concern. It’s the backbone of batch-to-batch predictability in sectors like adhesives, coatings, and specialty polymers.
Most suppliers provide this product at purities ranging from 98% to above 99%, measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The rest, under 2% or so, covers moisture, by-products, and trace organic residues. Manufacturers share detailed certificates of analysis, not just a broad purity figure—usually including limits on water content, color (measured by APHA standards), melting point, and specific gravity.
For someone working at a bench, a small shift in these numbers—say from 99.5% to 98%—may not sound huge. In practice, that difference can mean extra effort in purification steps or end up affecting the final cured strength of a resin. Impurities might react under curing conditions, leading to clouding or even failure in advanced composites.
Source reliability means everything. Responsible producers use closed-loop reactors and distillation processes that keep air and moisture out. Quality control relies on repeated lab checks—spectroscopy, titration, gas chromatography. Some suppliers test for metals at the parts per million level, since even background contamination from process vessels can mess with sensitive electronics or medical applications. This isn’t just about hitting a generic high purity label but holding up to real-world demands.
Documentation Supports ConfidenceHaving walked through supplier audits, I always look for comprehensive technical data sheets and batch-specific analyses. Trust grows when the supplier can show consistent values through six or eight consecutive batches, not just the one you’re about to purchase. Regulatory documentation, like RoHS or REACH statements, sometimes gets overlooked yet plays a big role for companies exporting into strict markets.
Entering a new supply partnership, I always push for a sample with complete certificates—not just a simple purity line. A direct lab check with in-house equipment never hurts before scaling up an order. In my experience, a few minutes spent reviewing SDS and consistency records keeps headaches at bay later, whether it’s regulatory surprise audits or troubleshooting an off-color batch in production.
It’s easy to take for granted that what’s listed on a website matches the drum arriving at the dock. Still, my colleagues and I have seen mismatches, and the cost—in time, lost batches, and trust with clients—hurts more than paying for documented, high-purity product upfront.
Some regions still struggle with supply chain verification. Third-party lab checks remain a practical solution, even though they add a layer of paperwork and time. Direct communication between the end user and supplier labs helps bridge gaps, smoothing misunderstandings over terminology or test methods. Collaborative audits, sharing not just finished sample data but details of raw feedstocks and processing aids, build a much clearer picture and stronger relationships over time.
Chemistry relies on small details, and purity is never just a number. Investing in reliable sources and robust verification keeps downstream products working, clients satisfied, and regulatory officers off your back.
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 2,2'-[Propane-1,3-diylbis(oxy)]diethanol |
| Other names |
2,2′-(1,3-Benzenediyloxy)diethanol 1,3-Benzenediol bis(2-hydroxyethyl) ether Resorcinol di(2-hydroxyethyl) ether Resorcinol bis(β-hydroxyethyl) ether Dihydroxyethyl resorcinol ether |
| Pronunciation | /ˌrɛˈsɔːrsɪnɒl bɪs ˈtuː haɪˌdrɒksiˈɛθɪl ˈiːθər/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 4707-47-5 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | `@chemical JSmol model string for "Resorcinol Bis (2-Hydroxyethyl) Ether"`: ``` C1=CC(=C(C=C1O)O)OCCOCCO ``` *(This is the SMILES string suitable for input into the JSmol 3D model viewer.)* |
| Beilstein Reference | 1207382 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:8718 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2106071 |
| ChemSpider | 20315 |
| DrugBank | DB14053 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 03ba8c2e-7a1f-4155-b7e0-d626af181360 |
| EC Number | 236-111-6 |
| Gmelin Reference | 1961280 |
| KEGG | C14365 |
| MeSH | D017380 |
| PubChem CID | 9225 |
| RTECS number | VL2275000 |
| UNII | 5N6M013C4K |
| UN number | UN 3082 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID1024809 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C14H18O4 |
| Molar mass | 286.32 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.296 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | Soluble |
| log P | 0.3 |
| Vapor pressure | <0.01 mmHg (20°C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 13.86 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 6.14 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -67.0·10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.565 |
| Viscosity | 250 – 450 mPa.s (at 25 °C) |
| Dipole moment | 4.72 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 328.8 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -914.7 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -4172.8 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | D11AX22 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful if swallowed or in contact with skin. Causes serious eye irritation. Causes skin irritation. |
| GHS labelling | GHS07, GHS09 |
| Pictograms | GHS07 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302, H315, H319 |
| Precautionary statements | Precautionary statements: P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-1-0 |
| Flash point | 232°C |
| Autoignition temperature | 400°C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 (rat, oral): 1820 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Rat Oral > 5000 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | RA3850000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not established |
| REL (Recommended) | 10 mg/m3 |