Chemical history doesn’t remember every compound, but Indole-5,6-Quinone has carved a unique place because of its deep connection to melanin research and biosynthetic pathways. Researchers began isolating this compound in the labs of the mid-20th century, recognizing its intermediate role during melanin formation in human skin. My early days reading about melanin synthesis laid bare the foundational impact of such intermediates. Certain enzymes, like tyrosinase, trigger a cascade where indoles start morphing into quinones — Indole-5,6-Quinone shows up right at this crucial stage, linking biochemistry with dermatology and neurology. Through archival research and investigative curiosity, this compound’s relevance to pigmentation disorders started emerging, making it a pivotal molecule for understanding both normal physiology and certain diseases.
Indole-5,6-Quinone isn’t something people bump into while shopping for lab chemicals. Specialists in pigment chemistry, skin biology, and environmental toxicology seek it out. It features both as a research standard and a reactant, offering value for analytical labs exploring pathways in melanogenesis or screening for environmental oxidants. Traditional product forms come as a dark solid, tending toward brown or red hues, signaling oxidation state right away. Suppliers keep purity levels above 95%, as small impurities cloud biological results. Its niche position stems from demand within targeted research fields, with each order often custom-packed to maintain stability and activity.
Indole-5,6-Quinone often appears as a fine crystalline powder, prone to air-induced changes. It boasts a molecular formula of C8H5NO2, weighing in around 147 g/mol. Water solubility stays low, due to aromatic structures and double bonds, shifting the practical focus to organic solvents or buffered systems for experimental work. The melting point falls below 250°C, decomposing instead of melting cleanly, hinting at delicate chemical balance. The molecule’s signature comes alive during spectroscopic scans, with visible absorption peaking close to 400 nm, signaling those quinonoid double bonds. That color acts as an instant visual marker; seasoned chemists recognize a subtle shift from dull purple to rusty brown as pH or redox changes take hold. Its stability suffers in sunlight or basic solutions, requiring storage in amber vials, inside cold cabinets, to keep spontaneous decomposition at bay.
A laboratory label for Indole-5,6-Quinone calls for precision. Precise mass, percentage purity (usually above 95%), and batch number remain essential. Expiry dates run short, underlining the compound’s reactivity. Labels must carry hazard pictograms: oxidation warning, skin and eye irritation, and acute toxicity where exposure exceeds certain thresholds. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) back up front labels, offering prevention, first aid, and spill response steps. To navigate compliance, research institutions require batch testing certifications — heavy metals content below 10 ppm, unreacted indole below 1%, and absence of volatile byproducts. Storage instructions mention dry, sealed conditions at 2-8°C, away from direct sunlight and sources of strong base.
Most lab syntheses draw on oxidation of 5,6-dihydroxyindole, a step central to tracking melanin formation. In one reliable method, 5,6-dihydroxyindole reacts with a mild oxidizer such as sodium periodate or ferricyanide in water or phosphate buffer at chilled temperatures. Preparation demands constant monitoring; over-oxidation brings unwanted polymers, while under-oxidation leaves starting material behind. Scaling beyond bench-top quantities raises troubles. Efforts to optimize eco-friendly processes, swapping hazardous oxidants for enzymatic ones, show promise but struggle with yield and repeatability. Chemists handling these syntheses benefit from hands-on experience. In my time synthesizing sensitive oxidation products, even the glassware’s cleanness nudged yields higher or lower. Reaction ends with careful extraction using dichloromethane, then solvent is evaporated under vacuum to leave the unstable quinone.
Indole-5,6-Quinone reacts at nearly every spot, making it a challenge and an opportunity for synthetic chemists. Its carbonyls open up conjugation reactions, such as Michael addition by nucleophilic amines or thiols, creating useful labelled probes for protein studies. The quinone ring accepts reduction, reverting to 5,6-dihydroxyindole under mild conditions — a back-and-forth that tracks cellular redox states. Substitution patterns allow for isotopic labeling, essential for metabolic tracing. Researchers link it to peroxidase enzymes or couple it to fluorophores, setting up real-time detection in tissue. But unchecked reactivity spawns side products, including mixed polymers and indole dimers, which complicate both analytical separation and biological interpretation.
Various names pop up, often requiring vigilance in sourcing or literature reviews. Synonyms include “5,6-Indolequinone,” “Indolequinone-5,6,” or, in biosynthetic circles, simply “Melanin Quinone Intermediate.” While CAS Registry Codes streamline identification during procurement, researchers trade synonyms based on historical traditions or the publication’s country of origin. Pharmaceutical and pigment chemistry literature sometimes use proprietary numbers or codes, so cross-referencing ensures accuracy during sample ordering and data compilation. Knowing each alias helps dodge mix-ups and drives sharper literature searches, especially across language barriers or less digitally indexed sources.
Labs handling Indole-5,6-Quinone invest in safety kits and regular staff briefings. Toxicity kicks in after moderate exposure — skin or eye contact causes burns and allergy-like irritation, and inhaling dust impacts the respiratory tract. Gloves, goggles, and lab coats become non-negotiable, backed by forced-air hoods for larger runs. Clean-up follows chemical waste protocols: quenching quinones with sodium sulphite or ascorbate before disposal, while all glassware runs through heavy-duty cleaning to avoid trace cross-contamination. Emergency eye-wash and spill kits sit nearby. Reporting any accidental exposures aligns with occupational safety rules, as cumulative low-level contact can drive sensitization and chronic effects. Training is less about memorizing rules and more about building habits, so even the fastest bench chemist learns to work with respect for this compound’s volatility and irritation hazards.
Indole-5,6-Quinone’s impact radiates well past basic research. Clinical dermatology banks on it to screen melanin formation modulators, tracing pigmentation imbalance origins in disorders like albinism or vitiligo. Neuroscience probes its role in neuromelanin deposits inside the brain, shedding new light on Parkinson’s disease progression. Analytical chemists use it to devise assays for oxidative stress or environmental pollutants. Pigment manufacturers study it to mimic natural hues and textures for sustainable colorants. Medical imaging teams link this compound to tracers and contrast agents, targeting tissues rich in melanin-like structures. Even material scientists eye it for conductive biomaterials, spinning ideas from its unique redox profile. So its utility threads from basic science to applied innovation, delivering tools for diagnosis, monitoring, and new therapies.
Active research still circles around analytical methods to better quantify, trace, and study Indole-5,6-Quinone in complex biological samples. Chromatography systems now reach sensitivity thresholds low enough for nanomolar detection in tissue, which helps map disease states more precisely. My direct work in analytical development taught me the challenge of separating quinone intermediates from hundreds of lookalike organics in a tissue extract; advances in HPLC-MS systems keep opening these frontiers. Scientists pursue new enzyme mimics, driving both cleaner synthesis and mechanistic discovery. Innovations in redox sensors use analogs of this quinone, which detect cell signaling changes. Research grants continue to support projects bridging synthetic chemistry, clinical studies, and real-world diagnostic device development, all anchored by this single molecule’s properties.
Toxicologists rate Indole-5,6-Quinone as moderately hazardous, warranting clear limits on concentration and exposure duration. Cell culture assays pick up oxidative stress and DNA strand breaks as primary risks, especially in cells lacking robust antioxidative defense. Chronic exposure cases report skin depigmentation and contact dermatitis in workers handling it improperly. Rodent studies flag neurotoxic outcomes at persistently high doses, raising concerns for neurological research. Real-world occupational hazards show up only in rare, unregulated settings — using engineered controls and PPE drops reported incidents near zero. Environmental impact remains minor; breakdown in soil or water produces more stable, less reactive products, though monitoring continues to track unintended side-products. Toxicity findings reinforce tight protocols rather than discouraging studied use, as clearly defined workflows greatly reduce human and environmental risk.
Interest in Indole-5,6-Quinone only grows as new applications take shape. Researchers want higher-purity, more stable analogs for advanced diagnostics and targeted therapeutics against pigmentation disorders or neurodegenerative diseases. Startups invest in modifying the molecule as a platform for redox-based sensors, aiming for smarter wearable health monitors. The green chemistry movement asks for synthesis routes avoiding harsh oxidants or toxic solvents, and biotechnologists respond with enzyme-driven methods showing early success. My sense from conferences is that multi-disciplinary teams will keep expanding the role of this modest molecule, drilling deeper into personalized medicine, advanced materials, and environmental monitoring. As understanding of biological oxidation advances, Indole-5,6-Quinone remains both a tool for inquiry and a stepping stone toward safer, adaptive health and materials solutions.
Indole-5,6-quinone doesn’t usually pop up outside science circles. For people not spending their days in a chemistry lab, it sounds obscure, but the stuff matters. Indole-5,6-quinone belongs to a group of compounds that come from oxidation of indoles, which are themselves important building blocks in both biology and industry. This compound does not exist on supermarket shelves, but its impact still trickles down to regular life.
Our hair and skin get their color from melanin. Indole-5,6-quinone acts as an intermediate in that natural coloring process. People with experience studying the biochemistry of skin sometimes see this compound pop up during explanations of pigmentation disorders. In conditions like albinism or vitiligo, pathways involving indole-5,6-quinone can go haywire. Too little or misplaced pigment shows the body’s chemistry depends on a bunch of small links like these.
A deeper understanding of indole-5,6-quinone gives doctors and researchers a shot at tackling skin condition treatments. For example, scientists have watched this intermediate during melanin synthesis for clues on designing better therapies for pigmentation problems or methods for preventing skin damage from environmental stress.
Chemists don’t stop at one function. Indole-5,6-quinone crops up while digging into neurodegenerative disorders too, since melanin-like substances in the brain can affect nerve health. Some researchers are looking into how buildup of these compounds might connect with diseases like Parkinson’s. Although not directly used as a treatment so far, indole-5,6-quinone points toward future therapies or early signs of disease.
Drug development gets complicated. People study pathways and sometimes design compounds to control how and where indole-5,6-quinone forms. The hope is future medicines could slow damage in brain or skin cells by blocking specific reactions along this line.
Beyond health, indole-5,6-quinone helps researchers interested in new materials. Natural melanins in animals create tough, UV-resistant coatings. Synthetic chemists try to mimic that by fiddling with indole-based quinones in the lab. They try to craft versatile coatings, organic electronics, or even more advanced sunscreens. Some attempts at bio-inspired polymers focus on molecules just like indole-5,6-quinone for their stability and protective benefits.
Not many people outside science need to know the chemical structure of indole-5,6-quinone. But from a practical perspective, this compound has links to health and technology that show up daily. That patch of missing pigment on someone’s hand, or a breakthrough in sun protection, often owes a debt to little-studied links like these. Following the chain from molecules to real-world effects keeps researchers busy and opens doors for better medicines and smarter materials.
People thinking about the future of health and technology should pay attention when chemists mention adventures with indole-5,6-quinone. Ideas start in the lab, but they don’t stay there forever—eventually, they grow into solutions the rest of us get to use.
Researchers using Indole-5,6-Quinone usually work with it in the context of pigment studies or organic chemistry. Even though it might look like a typical reagent on the shelf, this compound comes with real risks. Inhalation or skin contact can cause irritation. There’s also the risk that careless handling leads to spills or accidental exposure. These risks aren’t theoretical. Every chemist knows about someone who paid the price for neglecting basic safety rules.
Personal protective equipment never feels optional in the lab. For Indole-5,6-Quinone, a lab coat shields skin and regular clothes from stains or splashes. Eye protection isn’t just a formality—safety goggles keep dangerous dust or solution out of your eyes. Gloves (nitrile is a solid choice) keep your fingers safe and stop the chemical from absorbing into your skin. Working with chemicals always gets easier with these basics in play, and I’ve seen firsthand that a good pair of gloves can save a lot of regret.
The strong, sometimes unpleasant smell of chemicals like Indole-5,6-Quinone serves as a warning. Never handle it at an open bench, especially if anything involves dust or vapors. Use a well-ventilated fume hood. The airflow pulls any airborne particles away from your breathing space. Forgetting this step only takes a moment. One time I saw a colleague handle a similar quinone out in the open, and it led to coughing fits and a safety incident report.
Placing the container on the correct shelf matters more than people realize. Storing Indole-5,6-Quinone away from direct sunlight and high temperature reduces the risk of unwanted reactions. Chemicals should stay in clearly labeled, well-sealed bottles. Mixing up brown glass with clear or tossing it on a random shelf increases the odds of an accident. Every year, labs discard reagents simply because of poor labeling. That wastes money and creates hazards for others down the line.
After using Indole-5,6-Quinone, all surfaces and tools deserve attention. Water, soap, and sometimes specialized cleaning solutions keep the workspace clear. Disposal means following hazardous waste guidelines. Dumping leftovers down the drain not only breaks lab rules, but pollutes waterways. I always find that a little patience with waste containers pays off in peace of mind—no one wants hazardous chemicals lingering around unexpectedly.
Most accidents start with gaps in knowledge. Regular safety trainings remind everyone what can go wrong. Knowing emergency procedures, from eyewash stations to spill kits, gives people confidence to work safely. At my old lab, team safety walkthroughs with real-life scenarios helped new and old staff think through ‘what if’ moments before they became emergencies.
Good habits protect everyone sharing the workspace. This means double-checking labels, never rushing prep work, and speaking up if storage or equipment looks off. Regular equipment checks, good lighting, and well-stocked shelves keep small glitches from turning into big problems. Everyone brings home the lesson eventually: a little attention to safety details keeps research moving forward and people out of harm’s way.
Handling chemicals like Indole-5,6-Quinone challenges even experienced lab workers. This compound, a key intermediate in biological and industrial research, can degrade fast if kept in the wrong spot. Anyone who’s spilled a small fortune’s worth of reagent or come back to a cabinet full of clumped solids knows how quickly things can go sideways.
Setting aside expensive research supplies for just a moment, the risks posed by poor storage aren’t theoretical. Oxidative compounds are notorious for breaking down into useless foamy goop or worse, producing harmful byproducts. Indole-5,6-Quinone reacts with moisture and light, kicking off reactions that can skew results or make handling dangerous. Fresh out of grad school, I learned this rule the hard way: nothing ruins a week in the lab faster than discovering the main ingredient didn’t last in a warm, bright storeroom.
Every article or chemical data sheet gives the same three words: “cool, dry place.” Sounds simple until humidity spikes and the AC quits. Indole-5,6-Quinone stays stable in the dark, away from moisture, below room temperature. Invest in airtight containers made from glass, since plastic can interact with some sensitive chemicals. Toss in a few silica gel packs to trap stray water vapor. Assign a spot in a refrigerator reserved for chemicals, not the office snacks. Temperatures closer to 4°C work well; avoid freezer burn or frost buildup, since rapid temperature swings can encourage condensation. Most modern chemical cabinets feature UV-blocking doors—never underestimate the impact of even weak overhead lighting on long-term stability. In my own lab, we lost an entire batch because the shelves sat across from a big window. Adding blackout film and always sealing vials made the difference between wasted money and reliable results.
Precise labeling offers more than organization. Lot numbers, opening dates, and storage conditions help trace issues right away. Once a month, check for unusual smells, clumps, or color changes. No matter the expense, ditch anything that looks off—contamination risks aren’t worth a shortcut. Document control plays a crucial role in modern labs. Electronic logs or simple written records let everyone share knowledge about the quirks of each batch.
Reputable supply companies print storage and stability data right on the container. Still, guidelines alone don’t replace real-world vigilance. Teach newcomers to recognize the signs of breakdown and how to shield sensitive compounds from air and light. Stock emergency spill kits and PPE nearby, as indole derivatives have unpredictable toxicity when mishandled. Keep a chemical inventory so everyone knows how much remains. If a chemical hasn’t shifted in a year, consider discarding or replacing it. This approach cuts down on both waste and safety headaches.
Improved packaging can help. Vacuum-sealed ampoules or UV-opaque bottles might add cost, but cuts losses over time. Group storage of similar compounds often minimizes cross-contamination. If facilities allow, a controlled atmosphere chamber can take protection to the next level. Ultimately, the best storage plan relies on common sense, everyday vigilance, and staying informed about the compounds used. A careful approach keeps dangerous surprises at bay, saves money, and supports trustworthy research data.
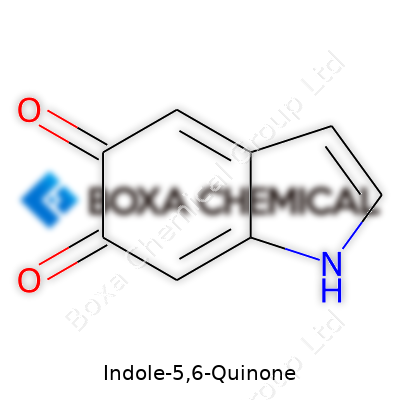
Indole-5,6-quinone stands out as a product formed during the oxidation of indole derivatives, which often shows up in biochemical pathways involving tryptophan or melanin synthesis. If you picture the familiar indole ring—two fused rings, a benzene ring joined to a pyrrole ring—now imagine swapping out hydrogen atoms for two carbonyl groups at the 5 and 6 positions. That shift creates the "quinone" part of this molecule, morphing the aromatic ring with two oxygen atoms double-bonded to carbon, sitting next to each other on the benzene piece of the structure.
The full chemical formula runs as C8H5NO2. The indole base offers flexibility for further reactions, and the quinone section ramps up its reactive power—especially important in enzymatic processes. In a lab, structural studies confirm the geometry through methods like NMR or crystallography, consistently showing that planar backbone and the reactive dione configuration at those two adjacent positions.
With this structure, indole-5,6-quinone doesn’t just rest on a shelf—it takes an active role in crucial processes, especially inside living organisms. Melanin biosynthesis depends on these oxidations to create the pigments protecting skin and eyes from UV light. I’ve learned from time in lab courses that the path from simple amino acids to complex pigments relies on a bunch of these carefully tuned oxidations, with intermediate quinones just like this popping up and driving the reactions ahead.
Research points to its role as a fleeting, highly reactive intermediate, catching researchers’ attention because the molecule often doesn’t stick around long. Scientists see bursts of it during in vitro experiments when they expose tryptophan or DOPA to oxidizing agents, tracing the brown or black pigment that inevitably results. Studies from groups working on pigment cell research report direct links between buildup of these quinones and certain pigmentation disorders, underlining its medical relevance.
Handling indole-5,6-quinone poses a challenge because exposure to air or mild reducing agents quickly moves it along to other products. During graduate research, any accidental oxygen exposure changed my reaction colors—telling me these intermediates don’t last long enough for easy purification. Most references, including peer-reviewed analytical chemistry work, suggest trapping or stabilizing such quinones right as they form, or else using rapid detection methods such as spectrophotometry or LC-MS.
Chemists keep improving their toolkits, forming derivatives or adding stabilizing groups to wrangle these unstable quinones for further study. Collaboration with analytical chemists has brought reliable detection into reach, with advances in techniques allowing even fleeting species to get their due attention in research papers. Developing in situ monitoring—measuring these compounds as they react—has opened new ground in understanding these complex biosynthetic chains.
The study of indole-5,6-quinone drives innovation across pigment biology, organic chemistry, and even material science. Getting clearer snapshots of this fleeting molecule opens the door for smarter therapies and synthetic pathways, benefitting researchers and patients in quietly significant ways. As more labs embrace tailored detection and creative stabilization tricks, the barriers to understanding this molecule in both health and material applications keep dropping.
Indole-5,6-quinone often pops up in science discussions, usually among chemists looking at how melanin forms in the body. It’s not something you’ll spot in everyday life, but researchers who handle pigments and study oxidative stress know this compound pretty well. Most of us have never heard of it, but its role in pigment biology means it sometimes shows up in biology textbooks or as part of big research projects.
Plenty of people, myself included, have puzzled over whether indole-5,6-quinone mixes well with water. Years of working in the lab have shown me that molecules with ring structures and few spots for hydrogen bonding tend to keep away from water. Water clings to things that give it a reason to hold on — think ionic or polar molecules. Indole-5,6-quinone carries an aromatic indole ring and two oxygen groups on neighboring carbons. Most would hope these oxygens make the molecule fit right in with water, but the story isn’t that simple.
Based on published research, indole-5,6-quinone doesn’t like to dissolve in water. The structure prefers organic solvents. Chemists have tried mixing it and found it settles or clumps, instead of thinning out. Pigment researchers, aiming to replicate natural melanin-like reactions, use organic solvents such as ethanol or even DMSO to move indole-5,6-quinone into solution. If you drop this compound in a glass of water, you won’t see it vanish — you’ll end up with gritty, brownish stuff sitting on the bottom.
Solubility often decides if something gets used or left behind. Back in grad school, I watched how research ideas stumbled when a compound refused to dissolve. If indole-5,6-quinone could mix with water, drug designers and pigment researchers would have a much smoother process. Water-based systems are gentler, cheaper, and safer for workers and the environment. By staying stubbornly out of aqueous solution, this molecule nudges scientists toward workarounds, including finding less toxic solvents — but these bring higher costs and tougher waste disposal.
Several chemical makers and biotechnology startups try to get around this issue. In practice, some use surfactants or co-solvents to coax indole-5,6-quinone into water, but that doesn’t give true solubility. Others pursue chemical tweaks, adding groups to make the molecule more water-friendly, though each tweak can change the compound’s effects and safety. A handful of smart researchers leverage nanoparticles to ferry the molecule through water, treating it as cargo. I've seen these attempts in meetings and read the papers — none feel like perfect, durable solutions just yet.
Maybe new chemistry will unlock ways to make indole-5,6-quinone join water solutions. For now, this stubborn brown pigment keeps reminding us how much a single property — like solubility — can decide the fate of a useful molecule. For those working in pigment science or trying to mimic natural colors, the challenge remains real. The search continues for smarter, safer ways to bring reluctant compounds like this one into water, opening up new experiments and safer products for everyone.
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 1H-indole-5,6-dione |
| Pronunciation | /ˈɪn.doʊl.faɪv.sɪks.kwɪˈnoʊn/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 548-83-4 |
| Beilstein Reference | 151941 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16133 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2106421 |
| ChemSpider | 130867 |
| DrugBank | DB08152 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 22be063b-14a8-4cbd-ab39-5b6fb7bb2677 |
| EC Number | 22.214.171.124 |
| Gmelin Reference | 87259 |
| KEGG | C05652 |
| MeSH | D017896 |
| PubChem CID | 70418 |
| RTECS number | NL2975000 |
| UNII | 5S6F9P467N |
| UN number | Not classified |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID6049634 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C8H5NO2 |
| Molar mass | 204.18 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark brown solid |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 1.421 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | slightly soluble |
| log P | 0.963 |
| Vapor pressure | 1.03E-06 mmHg at 25°C |
| Acidity (pKa) | 6.6 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 6.68 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -49.0×10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.809 |
| Dipole moment | 2.50 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 336.1 J/mol·K |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -19.8 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -1238.8 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful if swallowed, causes skin and eye irritation, may cause respiratory irritation |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS07 |
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H302: Harmful if swallowed. H315: Causes skin irritation. H319: Causes serious eye irritation. H335: May cause respiratory irritation. |
| Precautionary statements | P261, P264, P271, P273, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362+P364 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 1-2-2-☢ |
| Flash point | > 120°C |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 Intraperitoneal - mouse - 160 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | MT9810000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | Not Established |
| REL (Recommended) | 10-50 µM |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | Not listed |