The journey of 4-aminophenol traces back to the late 19th century, reflecting the rapid advancements within organic chemistry at the time. Scientists turned their focus toward derivatives of phenol, realizing the potential for those compounds in synthetic dye and pharmaceutical industries. The discovery of 4-aminophenol emerged from research on coal tar, which produced many aromatic amines and phenol derivatives. As demand for colorants and medicines soared, chemists advanced their methods, laying the groundwork for large-scale production. The synthesis of this compound opened doors for manufacturing analgesics and photographic developers, becoming a cornerstone for products familiar in daily life.
Known for its role as an intermediate, 4-aminophenol shows up across pharmaceutical, photographic, and dye industries. Often sold as white or slightly pinkish crystals, this chemical forms the backbone of several drugs, including paracetamol. Its reactivity and relative ease of modification keep it in demand, especially for companies aiming to streamline their synthetic routes. These industries have relied on its stability, moderate cost, and straightforward storage features, ensuring it stays relevant as processes modernize.
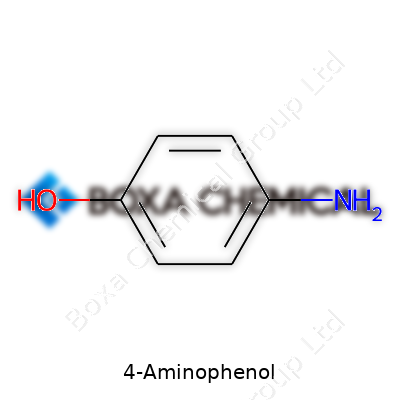
This compound comes as needle-shaped crystals or a crystalline powder, carrying a faint chemical odor. With a melting point of about 184°C and limited solubility in cold water, it dissolves better in hot water and is readily soluble in alcohol and ether. It stands out as a weak base, reacting with acids to form salts and with oxidizing agents to produce quinones or polymers. The presence of both amino and hydroxy groups on the benzene ring gives chemists two clear points for reactions, making it highly adaptable for new compounds or formulations. Its molecular formula, C6H7NO, and a molecular weight of 109.13 g/mol, allow for straightforward calculations and planning during synthetic work.
The industry often requires rigorous technical data for production and transport. Most 4-aminophenol powders get supplied in industrial bags with clear labeling for purity (often above 99%), moisture content, and byproducts. Quality standards depend on end-use, but pharmaceutical-grade material demands tight restriction on metallic impurities and residual solvents. Labels on commercial packages present hazard information, lot number, date of production, CAS number (123-30-8), and supplier details, all aligning with international trade requirements.
The standard industrial methods for 4-aminophenol preparation rely on either reduction of nitrophenols or hydrolysis of acetanilide derivatives. The most widely practiced method involves reducing 4-nitrophenol, using agents like iron filings and hydrochloric acid, or catalytic hydrogenation. Laboratories often use sodium borohydride under controlled temperature to produce smaller quantities. Companies value methods that offer high yields and minimal toxic waste. The alternative, hydrolysis of paracetamol or other acetanilides, comes in handy for pharmaceutical applications, especially when targeting high-purity products suited for drug production.
The amino group on this molecule reacts easily with acids, forming salts suitable for various further transformations. Its hydroxy group can take part in etherification, esterification, and oxidation, producing compounds like quinones or azo dyes. In the lab, diazotization of 4-aminophenol leads to coupling reactions central for dye stuff manufacturing. Chemists design modifications to tailor physical properties, enhance solubility, or introduce specific biological activities, reflecting years of accumulated research and creative adaptation by synthetic chemists.
The chemical community refers to this compound by a cluster of names, each hinting at its structure or historical use. Common synonyms include para-aminophenol, 4-hydroxyaniline, and p-aminophenol. Pharmaceutical and industrial catalogs may list it under NCI-C03413, or use translations depending on the country, making global commerce smoother. Each name carries its baggage of history and application, ensuring that those in the know understand its wide-reaching influence.
Handling 4-aminophenol demands careful attention because of its moderate toxicity and risk for skin and eye irritation. Material safety data sheets highlight the need for gloves, goggles, and ventilated workspaces. Industrial facilities enforce guidelines to limit dust formation and airborne particles, protecting long-term worker health. Storage protocols often include keeping the powder in dry, sealed containers, shielded from light, moisture, and strong oxidizers. Exposure limits rely on government regulations and company best practices, with routine training to keep accidents low and awareness high.
Pharmaceutical companies turn to this compound mainly for synthesizing paracetamol, a leading analgesic and antipyretic worldwide. Its role in photographic industry looms large, especially as a developer for black-and-white film. Dye manufacturers synthesize shades of blue, red, and black, leveraging the compound’s chemical versatility. Beyond these, specialty applications appear in hair dyes, corrosion inhibitors, and rubber antioxidants. Research efforts have branched into making new therapeutic agents and functional materials, showing the compound’s enduring flexibility across sectors.
Academic and industrial scientists keep pushing boundaries, exploring routes to produce the compound with less waste, lower temperatures, and greener reagents. Research looks at engineered catalysts for hydrogenation and greener reducing systems, hoping to scale down industrial hazards. Analytical chemists monitor for trace impurities and by-products, targeting pharmaceutical standards that grow stricter over time. Investigations into the compound’s chemical reactivity continue to turn up novel molecules, building potential for emerging technologies in electronics, energy storage, and specialty coatings where aromatic amines and phenols shine.
Toxicologists report that high doses or repeated exposure may cause methemoglobinemia – a blood disorder affecting oxygen delivery. Animal studies and case reports document the hazard of improper handling, underlining the need for controlled use. Research digs into the compound’s environmental fate, with efforts underway to improve wastewater management in factory discharges. Scientists recommend robust ventilation, personal protective equipment, and routine health monitoring for those working with the compound. They also urge for better labeling on finished products to ensure downstream users receive clear safety instructions, as consumer safety standards keep tightening.
If you ask those with years in fine chemicals or pharma manufacturing, they will tell you that compounds which respond well to modifications rarely fall out of favor, and 4-aminophenol fits this mold. Its array of functional groups gives researchers a flexible base for the next waves of innovation. Companies look at using renewable feedstocks, new processing techniques, and further integration with electronic and medical technologies. As markets shift toward sustainability, interest in bio-based or waste-minimized production methods will likely grow, keeping the compound relevant in plans for modern, responsible chemical manufacturing.
People rarely think about the chemicals behind common medicine or photographic paper, but 4-aminophenol plays a big role in both. Years back, I worked in a pharmacy storeroom. One of the surprising facts I learned was just how much goes into making simple painkillers like paracetamol. 4-aminophenol marks the start of that chain. Imagine sorting shipments and seeing industrial barrels labeled with a name unfamiliar to most, knowing inside sits the building block for the tablets families reach for every flu season.
The conversion of 4-aminophenol into paracetamol (or acetaminophen in North America) keeps the pain relief aisle fully stocked. Drug manufacturers use it in synthesis, reacting it with acetic anhydride. This method isn’t just old-fashioned chemistry—it’s a reliable process that delivers the same safe result every time. According to World Health Organization data, tens of billions of paracetamol tablets get produced every year, thanks to that dependable reaction. Without 4-aminophenol, fever reducers would be far less accessible across the world.
Besides medicine, darkroom fans and film photographers have counted on this compound for more than a century. Black-and-white developers often include 4-aminophenol or its derivatives. A friend once let me watch the developing process in a college photo lab—between the smell of chemicals and the red safelight, the real magic came from the crystals dissolving in water, slowly coaxing images out of the shadows. The way 4-aminophenol reacts with silver halides creates those sharp contrasts every analog photographer chases. Although digital photos now dominate, some artists still choose the slow, hands-on methods from the darkroom era.
In textile factories, dye chemistry calls for special skills. 4-aminophenol helps create certain dyes and pigments, giving wool or other fabrics deep, lasting color. Chemical journals point to its use in producing azo dyes, where it supplies the “amino” part of vivid molecules. These molecules latch onto fibers, providing not just color but durability against repeated washes. Back in college, a visit to a dyeing mill made the whole thing concrete for me—the rhythmic movement of fabrics through colored water tanks, with workers monitoring shades by eye.
4-aminophenol won’t pop up on safety labels in over-the-counter pills, but chemical manufacturers keep strict protocols handling it. Touching or inhaling raw powder causes irritation, so strict protective gear and ventilation stay standard in production plants. On the environmental side, companies and researchers push to make its synthesis cleaner, moving away from older, more polluting methods. Some labs develop ways to reuse catalysts or reduce harmful byproducts, aiming to keep waterways and communities safer. Because so many people rely on products made with this chemical, those steps aren’t just technical; they affect public health and local neighborhoods.
4-aminophenol often sneaks into chemistry classrooms in the form of simple reactions with iron or copper. Real-world uses like painkillers or photo prints bring those lessons to life. Students may grumble through the theory, but hands-on experiments let them trace how everyday objects connect back to one surprising ingredient. That experience stays with them, just as it did with me after my own brush with beakers and hotplates. Chemistry’s building blocks, often overlooked, shape the choices on drugstore shelves and the color in wool sweaters hanging in the closet.
4-Aminophenol shows up in plenty of labs and manufacturing plants, usually finding a role in making dyes, pharmaceuticals, and photographic chemicals. With that broad reach, you might assume it’s safe—or at least not that risky. The reality brings a different picture. Even a seasoned lab tech can slip up, especially if tired or distracted by deadlines. It only takes one moment with a poorly fitted glove, and that powder might sneak onto your skin or waft into your lungs. Exposure brings headaches, skin rashes, breathing problems, and even possible kidney damage after repeated contact.
Years spent working bench tops taught me to treat gloves, goggles, and coats like an extra layer of skin. Not the cheap gloves that rip when you grab a bottle, but real chemical-resistant ones. Splash-proof goggles, tightly sealed, prevent dust or liquid from irritating your eyes. A lab coat that covers arms and fastens fully adds another layer. Skipping safety glasses because “I’ll only be a minute” turns a small spill into a day ruined by an emergency room visit.
Nobody likes the sound of the fume hood fan droning on, but that hum signals cleaner air. Powdered chemicals go airborne with a single scoop, so proper ventilation keeps everyone breathing easier. I used to run reactions with the window open and a fan pointed out, but learned fast how a real fume hood beats makeshift setups. Labs and factories must keep hoods well-maintained. Checking airflow regularly keeps airborne hazards from sneaking up on you.
Ever try to find something in a cluttered chemical cabinet? Things get missed, bottles knock over, and suddenly there’s a pool of something you can’t identify. Storing 4-aminophenol in tightly sealed, properly labeled containers cuts confusion. I make it a habit to check labels before pouring or scooping out any substance. Clear hazard symbols and current dates help everyone avoid mistakes. Keeping incompatible chemicals far apart keeps small leaks from becoming fires or toxic clouds.
Accidents happen, but a quick response fixes most problems before they get out of hand. I once saw someone grab paper towels and dab at a spill, unsure if the chemical was hazardous. That’s not enough with something like 4-aminophenol. Prepared spill kits, absorbent materials, and proper disposal bins matter. Training regularly on how to respond—without panic—makes sure the team can handle small incidents before they escalate.
Plenty of safety manuals never leave their shelves. Reading them once at orientation doesn’t stick, especially for people who just want to get the job done. Hands-on training, regular drills, and reminders keep safety fresh in mind. When supervisors show safe habits every day, others follow. I remember rushing one day and a coworker quietly reminding me about my goggles. That moment stuck and probably kept me from injury more than any poster or checklist.
Safety with 4-aminophenol comes down to culture. If people know shortcuts won’t be tolerated, and if everyone watches out for each other, accidents drop. Reporting small spills without fear drives continuous improvement. Management can back this up by supplying enough PPE, keeping up with equipment maintenance, and acting on safety reports fast. Meeting legal regulations doesn’t just satisfy paperwork; it protects real people, every shift, every day.
4-Aminophenol has the chemical formula C6H7NO. Each molecule contains six carbon atoms, seven hydrogens, one nitrogen, and one oxygen atom. The molecular weight comes in at 109.13 g/mol. People working in labs or manufacturing keep this number close—accuracy matters, whether you're mixing reagents or scaling up for production.
The pharmaceutical sector leans on 4-aminophenol because it serves as a precursor in paracetamol (acetaminophen) synthesis. Anyone who checks the label on pain relievers probably depends, unwittingly, on this chemical’s reliability. The dye industry also puts it to work, crafting certain shades that end up on clothing and printed photographs. Most of the time, the end user never hears about the substrates behind their pain relief or vivid T-shirt, but these practical molecules are quietly doing their jobs.
I remember working with 4-aminophenol during undergraduate organic chemistry labs. Even a small spill can stain your hands brown, a trait that comes from its tendency to oxidize quickly. One mistake sticks out from my early days: not respecting the warning labels. It taught me the importance of gloves and good ventilation. The substance brings mild toxicity risks to the table. Skin contact and inhalation can lead to irritation, and larger exposures raise the stakes—methemoglobinemia can occur, which cuts off oxygen delivery in blood. Safety data sheets recommend thorough washing and eye protection. Practical lab habits and respect for health guidelines protect everyone, from first-year students to factory technicians.
Large-scale production of chemicals like 4-aminophenol raises crucial waste management questions. Factories have to manage wastewater loaded with organic byproducts. Proper treatment stops these from poisoning local streams. A few studies link uncontrolled discharge to aquatic toxicity. That means companies can’t cut corners, and regulators keep watch. Having seen chemical plant operations up close, I can say good engineering controls often prevent bigger problems. Industrial wastewater treatment often includes activated carbon and oxidation steps to neutralize contaminants. Community pressure and real consequences for rulebreakers drive better habits.
Chemists are always looking for ways to create 4-aminophenol with fewer steps and less hazardous waste. Research into catalytic hydrogenation and biosynthesis points toward these goals. Imagine swapping out harsh reagents for enzyme-based methods or closed-loop cycles that recapture solvents. Larger firms invest in these ideas because they cut costs and align with sustainability goals. It pays off long term, both in regulatory compliance and brand reputation.
Education makes a big difference in chemical safety. Every new technician and scientist working with these compounds needs training in both the science and the safety. Simple reminders, such as clear signage about personal protective equipment and mandatory engineering controls, help turn good intentions into practical routines. Over time, this approach lowers accident rates and builds trust with neighboring communities.
Anyone who’s spent time in a lab knows certain chemicals bring their own set of headaches. 4-Aminophenol fits that bill for many of us. It’s a useful compound, showing up in pharmaceuticals like paracetamol as well as in analytical chemistry work. But it also breaks down pretty fast if you treat it wrong. There’s no skipping over safety, not just for today but for the long haul. If you don’t take the right steps early, you end up with degraded material or, worse, a safety incident nobody expects.
4-Aminophenol doesn’t play nice with moisture. It clumps, degrades, and can turn into a sticky, useless mess. I’ve seen a container left open for just a day become lumpy and brown, riddled with oxidation. Oxygen speeds up the breakdown process, producing quinone-type structures and sometimes even causing the substance to overheat if larger amounts are exposed. Laboratories across industries all run into the same struggle: keeping 4-Aminophenol stable and pure matters for accurate results and worker protection.
Sealing is non-negotiable. Tightly screwed lids work, but for the best results, use containers with air-tight features, like glass jars with PTFE-lined caps. Plastic works only if it’s not going to interact with the chemical, but glass usually wins for long-term storage. Silica gel packs tossed inside serve well to distract any crawl-in humidity. Anyone thinking regular Tupperware or improvised bottles can cut it is risking more waste and a higher possibility for contamination.
Leaving 4-Aminophenol on a well-lit bench might seem harmless at first. In my first job, someone thought nothing of it until the powder darkened. Light and higher temperatures break down these molecules faster than a group of lab rats through a cracker barrel. I learned early that cool, dim shelves away from direct sunlight keep the chemical safer. Room temperature mainly works, but a dedicated chemical refrigerator, especially in tropical climates or older buildings without good ventilation, adds real peace of mind.
It’s more than just quality loss or unsightly stains. Decomposition can sometimes produce gases or byproducts that mess with nearby materials or personnel health. I still remember an incident where a nearby open solvent was affected, turning the whole corner of a storage room into an olfactory assault.
Labels feel mundane, but sloppy handwriting or neglect here can lead to mixes between similar-looking powders. I’ve watched accidents happen over missing dates or unreadable shorthand. Full chemical names, hazard information, and the date the material came in should follow any storage system. Adding expiration dates, even conservative ones, stops product that’s well past its prime from getting into a reaction vessel. No one wants a synthesis ruined—or worse, someone’s health jeopardized—over a labeling shortcut.
Good practice in storing 4-Aminophenol means less money wasted, fewer batch failures, and safer workspaces. Glass jars in cool, dry, well-ventilated rooms, away from sunlight, paired with silica gel, clear labels, and a strong habit of auditing the shelves pays out every single month. I’ve worked with teams that ran into avoidable headaches because they cut corners, and those lessons stick. Keeping things secure and clear today keeps the work rolling smooth for everyone tomorrow.
4-Aminophenol often works behind the scenes in some of the most important products we count on every day. If you have dyed your hair or developed old-school photographs, you’ve probably had contact with this chemical, even if you’ve never heard its name. Its signature benefit shows up in its power to transform other chemicals, giving it a special spot in the toolbox of both manufacturing and laboratory science.
Think about pain relief. Over-the-counter acetaminophen—better known as paracetamol—wouldn’t exist without 4-aminophenol. Chemists rely on it when they build the active ingredient for these medicines. Its molecular structure lets it react cleanly to make paracetamol, a process that runs on a global scale. Paracetamol’s massive popularity in homes and hospitals speaks for itself, especially when fevers and aches hit out of the blue. The World Health Organization has listed this medicine as one of its “essential medicines,” reflecting just how big its impact has become.
Walk into any hair salon. The chance is high that products on the shelves started with 4-aminophenol. This chemical helps deliver strong, lasting shades in permanent hair dyes. Companies choose it because of the way it holds on to color and reacts safely, making it a dependable piece of the dye puzzle. Textile and leather industries echo this use, reaching for this compound to dye fabrics and skins with vivid, durable hues. Its ability to build complex dye molecules brings real value, cutting costs while allowing for creative freedom.
Photography used to hang on chemicals even more than it does today. In black-and-white film, 4-aminophenol played the role of a reducing agent, turning exposed film into clear, striking images. Some hobbyists and artists stick to traditional film to this day, fueling a small but dedicated demand for classic developers made from this compound. These formulas give a unique look that even the sharpest digital filters rarely imitate.
Researchers use 4-aminophenol as a building block to create other chemicals, setting up reactions that stretch from polymer science to surface treatments. Its predictable reactivity and ready availability help scientists test new theories or design specialty products. In my experience, labs often pick it for method development because it tends to behave reliably, even under tough conditions.
It’s important to remember that industrial chemicals don’t just vanish after use. Waste from dye factories and pharmaceutical plants can include residues. Companies must treat this waste carefully to keep local water and soil clean. Regulatory frameworks keep tightening, making producers invest in greener methods and closed-loop systems to trap and neutralize residues. Recycling programs and continuous monitoring make a big difference, but ongoing innovation plays an even bigger role in keeping workers and neighborhoods safe.
Hidden in everything from pill bottles to photo negatives, 4-aminophenol continues to shape both established and emerging industries. As the call for greener production grows louder, sustainable alternatives and new methods are gaining ground. Still, for now, few molecules can match the versatility and trust that this one has earned through hands-on experience in factories and labs the world over.
| Names | |
| Preferred IUPAC name | 4-Aminophenol |
| Other names |
4-Hydroxyaniline p-Aminophenol p-Hydroxyaniline para-Aminophenol |
| Pronunciation | /ˈfɔːr əˌmiːnəˈfiːnɒl/ |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 123-30-8 |
| Beilstein Reference | 1209224 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:1588 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1408 |
| ChemSpider | 529 |
| DrugBank | DB06824 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.054.475 |
| EC Number | 205-255-0 |
| Gmelin Reference | 84119 |
| KEGG | C01379 |
| MeSH | D000662 |
| PubChem CID | 748 |
| RTECS number | SJ8570000 |
| UNII | Z97M7R6KZ9 |
| UN number | UN2811 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | DTXSID2022802 |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H7NO |
| Molar mass | 109.13 g/mol |
| Appearance | White to light purple crystalline solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.293 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in water | Moderately soluble |
| log P | 0.47 |
| Vapor pressure | 5.3E-4 mmHg (25°C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.3 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 8.07 |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -56.0·10⁻⁶ cm³/mol |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.680 |
| Viscosity | 0.954 cP at 50 °C |
| Dipole moment | 5.75 D |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std molar entropy (S⦵298) | 115.4 J·mol⁻¹·K⁻¹ |
| Std enthalpy of formation (ΔfH⦵298) | -26.4 kJ/mol |
| Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) | -1146.4 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| ATC code | N02BE04 |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Harmful if swallowed, causes skin and eye irritation, may cause allergic skin reaction, harmful to aquatic life. |
| GHS labelling | GHS02, GHS07 |
| Pictograms | GHS06,GHS05 |
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | Harmful if swallowed. Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation. |
| Precautionary statements | Precautionary statements: P261, P280, P305+P351+P338, P312 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | 2-1-1 |
| Flash point | 145°C |
| Autoignition temperature | 300°C |
| Lethal dose or concentration | LD50 oral rat 375 mg/kg |
| LD50 (median dose) | LD50 (median dose): Oral-rat LD50: 375 mg/kg |
| NIOSH | SN2100000 |
| PEL (Permissible) | 5 mg/m3 |
| REL (Recommended) | 7.5 mg/kg bw |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | No IDLH established. |